Fanshawe’s chosen system for Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAl) is the Microsoft Copilot Chat Assistant (Enterprise Version). This software is included in our site license for all employees and students, so that the college community may leverage Al-powered productivity features such as content generation, document summarization, and creative media generation. This product has a data protection guarantee: conversations with Copilot are private, will not be saved, and will not be used to train the software. The use of other GenAI tools, which may be insecure and mine data as part of their business model, are not authorized or supported by Fanshawe.
Copilot Setup / Installation
- Access to Copilot for Web is available by clicking the Copilot icon in the top-right corner when using the Microsoft Edge browser.
From any Internet browser, you can also follow the sequence here to log into copilot.microsoft.com.
What Copilot Can Do
Copilot’s most popular feature is its chat function. Because of its access to a large subset of public human knowledge, it can act as a highly knowledgeable assistant, offering insights and information across a wide range of topics without replacing the role or quality of the subject matter expert – you. Using the chat function, a professor might use Copilot to:
- Suggest a new way of introducing a lesson
- Analyse whether an activity is aligned with learning outcomes
- Suggest the number of written words or recorded minutes are appropriate for a presentation
- Create a bank of discussion or quiz questions based on a topic or outcome
- Add a section to a reading to incorporate a new event, or to consider marginalized populations, or indigenous ways of learning, or a global perspective
- Paraphrase text so that is clear, concise, and grammatically accurate
- Highlight knowledge gaps or bias in your presentation of an idea
Copilot can also do tasks based on an uploaded file or webpage content as follows:
- Documents (PPT, DOCX, etc.): summarize, synthesize, critique, modify or generate new content
- Images (JPG, PNG, etc.): describe, identify objects or people, recognize text, apply filters
- Audio & Video (MP3, MP4, MOV, etc.): Identify content or themes, critique or make editing suggestions, create a transcript
Additional examples and sample prompts will be provided in the Teaching with AI section. Note: users should review and verify all Copilot responses before using them. More on this later…
Prompting Essentials
Prompts are instructions or input that a person gives Copilot to generate a response. Prompts can be:
- Simple and factual: “When was the last time the Leafs won the cup?”
- Open ended: “Why haven't the Leafs won the cup since 1967?”
- Predictive: “What do the Leafs need to do to win the Stanley Cup in the future?”
- Task-oriented: “Write me a program that calculates their odds of winning this year based on historical data, and then create a picture that symbolizes how likely this would be.”
The value of Generative AI is often realised in its ability to conduct a complex task across a series of prompts, i.e., a conversation, in which the user and AI prototype the request together until the desired goal is achieved. Doing this process well is known as prompt engineering, and with Copilot, there are ways of making a response that arrives at useful results quickly.
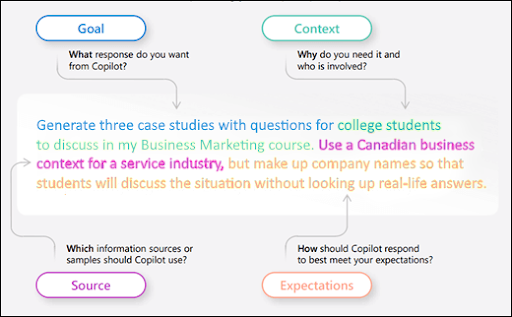
These are the four main “ingredients” that contribute to an effective prompt:
- Goal: what is your desired result or purpose?
Generate three case studies with questions…
Write a conclusion that includes a call to action …
Create a five-point summary… - Context: who are you, and why are you making this request?
…for college students to discuss in my Business Marketing Course…
…to ask a group of students in my course about being past a deadline…
…for a student with an accommodation who cannot process big chunks of text… - Source: what should the answer be based on?
…Use a Canadian Business context for a service industry…
…Start with the text from my email below.
…Based on my micro-lecture video attached here. - Expectations: what should the format, style, or tone of your answer look like?
…but make up company names so that students will discuss the situation without looking up real-life answers.
…the tone should be professional, but it should be clear that I am disappointed.
...you can paraphrase to remove filler and to ensure that it is easy to understand for this student.
Every prompt does not need to have all four ingredients, but for complex tasks, you will get a better first result the more accurately you describe the request fully using these categories. See below for more advanced aspects of using Copilot successfully.
Helpful Prompting Tips
Have a conversation
If your request is complex, or if the response isn’t correct the first time, it is more effective to clarify or ask for improvements instead of starting over. This includes multi-step tasks related to earlier parts of the conversation. “The description you produced here is too complex for my first-year college students. Simplify the language, reduce it to under 500 words, and then use that result to produce 10 true or false questions I can use during class.”
One topic – one chat
Because Copilot remembers the thread of the active conversation, it’s best to begin a “new chat” when you switch to a separate topic. This will ensure that the AI is not being informed by irrelevant details as context for a new request.
Give examples
If you are looking for additional examples, including known qualities in your prompt can help clarify your meaning. “Can you list some famous Canadians like Celine Dion, Ryan Reynolds, Sandra Oh, or Wayne Gretzky that international students might be familiar with?”
Use proper grammar
Generative AI uses the phrasing, syntax, and structure of your request to determine what you’re asking before it begins searching for a request. More than how a search engine mostly looks at the words themselves, this tool relies more holistically on your question to determine an appropriate response. Minor spelling or grammar errors are rarely a problem, but significant mistakes in your request reduce the likelihood of a useful result.
Be professional
Similarly, because this technology uses a snapshot of your response as a basis, your request should mirror the tone and style that you expect to see in the response. In other words, the style of your request is data to an AI. Rumours that AIs prefer nice people are Hollywood science fiction (for now), but making a rude, terse, and informal request is unlikely to generate a polite, well-reasoned, and professional result. You get what you ask for.
Don't contradict
Generative AI can get very confused if your prompt contradicts itself, for example, “Provide a brief, 7-page summary that has a professional but casual tone.” In cases where your request might seem this way, it is better to have a simpler prompt that describes (perhaps after the initial answer) aspects that are different from the norm, e.g.
“…The tone should be formal-professional, but there should be humour in the conclusion.”
“…Keep all summary sections under 100 words but describe the recommendations in more detail.”
Use quotation marks
To ensure that Copilot makes changes to a specific part of your input, you can use quotation marks so that it understands an exact context. For instance, you might tell it the following:
Edit the email so that the second paragraph begins with this sentence: "Your group needs to come up with three different solutions to the problem you read about in the case study."
Ensure humanity
Last but not least, remember that Copilot is a digital assistant that Fanshawe hopes will help you discover efficiencies and opportunities in your teaching role. Your touch is required as the final step of any process where AI is used. Using your expertise, make sure that the responses to your prompts are accurate and fair; rehumanize them by adding your unique voice and a touch of humor. This ensures that the final output is not only correct but also engaging and relatable for your audience.